Cùng với danh từ, tính từ và trạng từ, các loại động từ (Verb) trong tiếng Anh là một loại từ loại rất thông dụng mà chắc chắn ai cũng đã từng nghe qua. Trong bài viết ngày hôm nay, duhoctms.edu.vn sẽ giúp các bạn có cái nhìn tổng quan về những động từ tiếng Anh nhé.
1. Động từ trong tiếng Anh – verb là gì?
Động từ (verb) được định nghĩa là các từ thể hiện một hành động hoặc trạng thái của bản thể…
Cùng với chủ ngữ, động từ là thành phần bắt buộc, cần phải có trong câu. Một cách khác động từ là hành động hoặc trạng thái của câu.

Khi viết một câu hay mệnh đề, chúng ta cần bao gồm một động từ, sử dụng để nói đến hành động (những gì làm) và trạng thái của hiện tượng (mọi thứ như thế nào).
Ví dụ minh hoạ:
- To write ⇒ viết
- To anticipate ⇒ mong chờ
- To love ⇒ yêu
- To smoke ⇒ hút
2. Vị trí của động từ (Verb) trong câu
Trong tiếng Anh, động từ (Verb) có thể nằm ở rất nhiều vị trí khác nhau trong câu và trong một câu cũng có thể có rất nhiều động từ. Nghe có vẻ khá rắc rối nhưng sẽ rất đơn giản nếu bạn nắm rõ nguyên tắc sau:
Trong một câu đơn hoặc một mệnh đề, gắn với một chủ ngữ thì chỉ có một động từ được chia thì, các động từ còn lại thì sẽ được chia theo dạng.
Ví dụ minh hoạ:
- He loves to read books during the weekend.
⇒ Anh ấy yêu thích việc đọc sách mỗi cuối tuần.
⇒ Động từ “love” là động từ được chia thì hiện tại đơn (simple tense) còn “read” được chia theo dạng to + nguyên mẫu.
- I look forward to hearing from you soon
⇒ Tôi mong sớm nhận được hồi âm từ bạn.
⇒ Động từ “love” là động từ được chia theo thì hiện tại đơn (simple tense) còn “hearing” được chia theo dạng V-ing.
- They are dancing and singing outside to celebrate their father’s birthday
⇒ Họ đang nhảy và hát bên ngoài để chúc mừng sinh nhật cha của họ.
⇒ Chúng ta có 2 động từ “dance” và “sing” được chia theo thì hiện tại tiếp diễn. Tuy nhiên, đây là câu ghép từ 2 câu đơn: They are dancing outside to celebrate their father’s birthday và they are singing outside to celebrate their father’s birthday.
⇒ “Celebrate” là động từ được chia theo dạng to + nguyên mẫu.
Từ những ví dụ trên, bạn có thể suy ra rằng động từ chia ở thì (tense) sẽ đứng sau chủ ngữ còn động từ chia ở dạng (form) sẽ được sắp xếp theo một công thức.
3. Những loại động từ trong tiếng Anh
Do số lượng khổng lồ trong ngôn ngữ Anh, có rất nhiều cách để chúng ta phân loại các động từ tiếng Anh tùy theo chức năng của nó. Tuy nhiên, chúng ta có những cách phổ biến để phân loại động từ trong tiếng Anh như sau:
3.1. Động từ thường (Ordinary verbs) và trợ động từ (Auxiliary verbs)
Giống như tên gọi của nó, trợ động từ (auxiliary verbs) là các động từ được sử dùng để hỗ trợ các động từ trong tiếng Anh khác nhằm tạo thành một câu có cấu trúc chính xác và dễ hiểu. Trợ động từ thường sẽ có 3 loại chính như sau:

- To be, to have: là 2 trợ động từ vừa có thể sử dụng làm trợ động từ vừa là động từ thường.
- Động từ khiếm khuyết (modal verbs): là các động từ sử dụng để miêu tả khả năng, sự chắc chắn, nghĩa vụ, sự cho phép (can, may, shall, will, ought to, must, v.v). Cùng chúng mình tìm hiểu vậy sau can là động từ gì ở phần 4 nhé!
- Một số động từ đặc biệt: có trường hợp dùng làm động từ thường, có trường hợp dùng làm trợ động từ. Một số ví dụ: to dare, to need, to do, used to.
Tất cả các động từ còn lại được gọi là động từ thường (ordinary verbs).
Dưới đây là danh sách 23 trợ động từ (Auxiliary verbs) thường gặp trong tiếng Anh.
| STT | Auxiliary verbs | Nghĩa |
| 1 | Am | Là |
| 2 | Is | Là |
| 3 | Are | Là |
| 4 | Were | Là |
| 5 | Being | Hiện tại |
| 6 | Been | Là |
| 7 | Has | Có |
| 8 | Have | Có |
| 9 | Had | Có |
| 10 | Shall | Nên |
| 11 | Will | Sẽ |
| 12 | Should | Nên |
| 13 | May | Có thể |
| 14 | Might | Có thể |
| 15 | Must | Cần phải |
| 16 | Could | Có thể |
| 17 | Does | Làm |
| 18 | Do | Làm |
| 19 | Was | Là |
| 20 | Be | Thì là ở |
| 21 | Did | Làm |
| 22 | Would | Sẽ |
| 23 | Can | Có thể |
3.2. Ngoại động từ (Transitive verbs)
Về mặt ngữ pháp, ngoại động từ (Transitive verbs) là các động từ bắt buộc phải có tân ngữ đi sau trong câu không bị tối nghĩa.
Ví dụ minh hoạ:
- We arrived at the classroom door with only seven seconds to spare.
⇒ Chúng tôi vừa kịp đến lớp 7 giây trước khi quá trễ.
⇒ Động từ “arrive” phải đi kèm với tân ngữ (at the classroom) thì câu văn mới có ý nghĩa.
- To escape the midday sun, the cats lie in the shade under the trees.
⇒ Để thoát khỏi ánh mặt trời giữa trưa, những con mèo nằm trong bóng râm dưới tán cây.
⇒ Động từ “lie” đi kèm với tân ngữ (in the shade) thì câu văn mới có ý nghĩa đầy đủ.
Dưới đây là danh sách 18 ngoại động từ (Transitive verbs) thường gặp kèm với ngữ nghĩa tiếng Việt:
| STT | Transitive verbs | Nghĩa |
| 1 | ate | ăn |
| 2 | borrow | vay |
| 3 | bring | mang đến |
| 4 | buy | mua |
| 5 | clean | dọn dẹp |
| 6 | discuss | bàn luận |
| 7 | feed | cho ăn |
| 8 | gave | đã đưa cho |
| 9 | hug | ôm |
| 10 | left | bên trái |
| 11 | offer | phục vụ |
| 12 | praise | khen |
| 13 | prime | nguyên tố |
| 14 | promise | lời hứa |
| 15 | send | gửi |
| 16 | tease | trêu chọc |
| 17 | want | muốn |
| 18 | write | viết |
3.3. Nội động từ (Intransitive verbs)
Ngược lại, nội động từ (intransitive verbs) trong tiếng Anh không cần phải có tân ngữ do hành động mà động từ đó đang miêu tả không tác động trực tiếp lên bất kỳ đối tượng nào.

Ví dụ minh hoạ:
I was sleeping when my cats decided to scream at me at 3 in the morning.
⇒ Tôi đang ngủ thì mèo của tôi quyết định hét vào mặt tôi lúc 3 giờ sáng
⇒ Động từ sleep không cần phải có tân ngữ đi theo sau mà vẫn không bị tối nghĩa.
Bên dưới là 50 nội động từ (Intransitive verbs) trong tiếng Anh thường gặp nhất.
| STT | Transitive verbs | Nghĩa tiếng Việt |
| 1 | Agree | Đồng ý |
| 2 | Appear | Hiện ra |
| 3 | Arrive | Đến |
| 4 | Become | Trở nên |
| 5 | Belong | Thuộc về |
| 6 | Depend | Tùy theo |
| 7 | Die | Chết |
| 8 | Disappear | Biến mất |
| 9 | Exist | Hiện hữu |
| 10 | Explode | Nổ tung |
| 11 | Fade | Phai màu |
| 12 | Fall | Ngã |
| 13 | Fast | Nhanh |
| 14 | Float | Trôi nổi |
| 15 | Fly | Ruồi |
| 16 | Go | Đi |
| 17 | Grow | Mọc lên |
| 18 | Happen | Xảy ra |
| 19 | Have | Có |
| 20 | Jump | Nhảy |
| 21 | Lead | Chỉ huy |
| 22 | Learn | Học |
| 23 | Left | Bên trái |
| 24 | Lie (recline or tell an untruth) | Nói dối (ngả lưng hoặc nói điều không đúng sự thật) |
| 25 | Listen | Nghe |
| 26 | Live | Trực tiếp |
| 27 | Look | Nhìn |
| 28 | Move | Di chuyển |
| 29 | Occur | Xảy ra |
| 30 | Panic | Hoảng loạn |
| 31 | Party | Buổi tiệc |
| 32 | Pause | Tạm ngừng |
| 33 | Relax | Thư giãn |
| 34 | Rise | Trỗi dậy |
| 35 | Roll | Cuộn |
| 36 | Run | Chạy |
| 37 | Skip | Nhảy |
| 38 | Sleep | Ngủ |
| 39 | Slide | Trượt |
| 40 | Smell | Đánh hơi |
| 41 | Smile | Nụ cười |
| 42 | Spin | Quay |
| 43 | Stand | Đứng |
| 44 | Stay | Ở lại |
| 45 | Swim | Bơi |
| 46 | Swing | Lung lay |
| 47 | Wait | Đợi đã |
| 48 | Wake | Thức dậy |
| 49 | Walk | Đi bộ |
| 50 | Work | Công việc |
3.4. Động từ có quy tắc (Regular verbs)
Động từ có quy tắc (regular verbs) trong tiếng Anh là các động từ được chia thì theo một quy tắc nhất định.
Bên dưới là danh sách các động từ có quy tắc (Regular verbs) thường gặp trong tiếng Anh.
| BASE FORM | SIMPLE PAST | PAST PARTICIPLE |
| Accept | Accepted | Accepted |
| Achieve | Achieved | Achieved |
| Add | Added | Added |
| Admire | Admired | Admired |
| Admit | Admitted | Admitted |
| Adopt | Adopted | Adopted |
| Advise | Advised | Advised |
| Agree | Agreed | Agreed |
| Allow | Allowed | Allowed |
| Announce | Announced | Announced |
| Appreciate | Appreciated | Appreciated |
| Approve | Approved | Approved |
| Argue | Argued | Argued |
| Arrive | Arrived | Arrived |
| Ask | Asked | Asked |
| Assist | Assisted | Assisted |
| Attack | Attacked | Attacked |
| Bake | Baked | Baked |
| Beg | Begged | Begged |
| Behave | Behaved | Behaved |
| Boil | Boiled | Boiled |
| Borrow | Borrowed | Borrowed |
| Brush | Brushed | Brushed |
| Bury | Buried | Buried |
| Call | Called | Called |
| Challenge | Challenged | Challenged |
| Change | Changed | Changed |
| Chase | Chased | Chased |
| Cheat | Cheated | Cheated |
| Cheer | Cheered | Cheered |
| Chew | Chewed | Chewed |
| Clap | Clapped | Clapped |
| Clean | Cleaned | Cleaned |
| Collect | Collected | Collected |
| Compare | Compared | Compared |
| Complain | Complained | Complained |
| Confess | Confessed | Confessed |
| Construct | Constructed | Constructed |
| Control | Controlled | Controlled |
| Copy | Copied | Copied |
| Count | Counted | Counted |
| Create | Created | Created |
| Cry | Cried | Cried |
| Cycle | Cycled | Cycled |
| Damage | Damaged | Damaged |
| Dance | Danced | Danced |
| Deliver | Delivered | Delivered |
| Destroy | Destroyed | Destroyed |
| Divide | Divided | Divided |
| Drag | Dragged | Dragged |
| Earn | Earned | Earned |
| Employ | Employed | Employed |
| Encourage | Encouraged | Encouraged |
| Enjoy | Enjoyed | Enjoyed |
| Establish | Established | Established |
| Estimate | Estimated | Estimated |
| Exercise | Exercised | Exercised |
| Expand | Expanded | Expanded |
| Explain | Explained | Explained |
| Fry | Fried | Fried |
| Gather | Gathered | Gathered |
| Greet | Greeted | Greeted |
| Guess | Guessed | Guessed |
| Harass | Harassed | Harassed |
| Hate | Hated | Hated |
| Help | Helped | Helped |
| Hope | Hoped | Hoped |
| Identify | Identified | Identified |
| Interrupt | Interrupted | Interrupted |
| Introduce | Introduced | Introduced |
| Irritate | Irritated | Irritated |
| Joke | Joked | Joked |
| Jump | Jumped | Jumped |
| Kick | Kicked | Kicked |
| Kill | Killed | Killed |
| Kiss | Kissed | Kissed |
| Laugh | Laughed | Laughed |
| Lie | Lied | Lied |
| Like | Liked | Liked |
| Listen | Listened | Listened |
| Love | Loved | Loved |
| Marry | Married | Married |
| Measure | Measured | Measured |
| Move | Moved | Moved |
| Murder | Murdered | Murdered |
| Need | Needed | Needed |
| Obey | Obeyed | Obeyed |
| Offend | Offended | Offended |
| Offer | Offered | Offered |
| Open | Opened | Opened |
| Paint | Painted | Painted |
| Park | Parked | Parked |
| Phone | Phoned | Phoned |
| Pick | Picked | Picked |
| Play | Played | Played |
| Pray | Prayed | Prayed |
| Printed | Printed | |
| Pull | Pulled | Puled |
| Punch | Punched | Punched |
| Punish | Punished | Punished |
| Purchase | Purchased | Purchased |
| Push | Pushed | Pushed |
| Question | Questioned | Questioned |
| Race | Raced | Raced |
| Relax | Relaxed | Relaxed |
| Remember | Remembered | Remembered |
| Reply | Replied | Replied |
| Retire | Retired | Retired |
| Return | Returned | Returned |
| Rub | Rubbed | Rubbed |
| Scold | Scolded | Scolded |
| Select | Selected | Selected |
| Smoke | Smoked | Smoked |
| Snore | Snored | Snored |
| Stare | Stared | Stared |
| Start | Started | Started |
| Study | Studied | Studied |
| Talk | Talked | Talked |
| Thank | Thanked | Thanked |
| Travel | Travelled | Travelled |
| Trouble | Troubled | Troubled |
| Type | Typed | Typed |
| Use | Used | Used |
| Visit | Visited | Visited |
| Wait | Waited | Waited |
| Walk | Walked | Walked |
| Want | Wanted | Wanted |
| Warn | Warned | Warned |
| Wink | Winked | Winked |
| Worry | Worried | Worried |
| Yell | Yelled | Yelled |
3.5. Động từ bất quy tắc (Irregular verbs)
Động từ bất quy tắc (irregular verbs) trong tiếng Anh là các động từ không thêm “d” hoặc “ed” vào cuối từ như trong thì quá khứ đơn hay trong quá khứ V-3. Bởi vì nó không được chia như các động từ có quy tắc thông thường, nên cách duy nhất để ghi nhớ đó là học thuộc lòng bảng động từ bất quy tắc một cách đầy đủ nhất.

Bên dưới là danh sách các động từ bất quy tắc (Irregular verbs) thường gặp
| V1 Base Form | V2 Past Simple | V3 Past Participle |
|---|---|---|
| awake | awoke | awoken |
| be | was, were | been |
| beat | beat | beaten |
| become | became | become |
| begin | began | begun |
| bend | bent | bent |
| bet | bet | bet |
| bid | bid | bid |
| bite | bit | bitten |
| blow | blew | blown |
| break | broke | broken |
| bring | brought | brought |
| broadcast | broadcast | broadcast |
| build | built | built |
| burn | burned or burnt | burned or burnt |
| buy | bought | bought |
| catch | caught | caught |
| choose | chose | chosen |
| come | came | come |
| cost | cost | cost |
| cut | cut | cut |
| dig | dug | dug |
| do | did | done |
| draw | drew | drawn |
| dream | dreamed or dreamt | dreamed or dreamt |
| drive | drove | driven |
| drink | drank | drunk |
| eat | ate | eaten |
| fall | fell | fallen |
| feel | felt | felt |
| fight | fought | fought |
| find | found | found |
| fly | flew | flown |
| forget | forgot | forgotten |
| forgive | forgave | forgiven |
| freeze | froze | frozen |
| get | got | got (sometimes gotten) |
| give | gave | given |
| go | went | gone |
| grow | grew | grown |
| hang | hung | hung |
| have | had | had |
| hear | heard | heard |
| hide | hid | hidden |
| hit | hit | hit |
| hold | held | held |
| hurt | hurt | hurt |
| keep | kept | kept |
| know | knew | known |
| lay | laid | laid |
| lead | led | led |
| learn | learned or learnt | learned or learnt |
| leave | left | left |
| lend | lent | lent |
| let | let | let |
| lie | lay | lain |
| lose | lost | lost |
| make | made | made |
| mean | meant | meant |
| meet | met | met |
| pay | paid | paid |
| put | put | put |
| read | read | read |
| ride | rode | ridden |
| ring | rang | rung |
| rise | rose | risen |
| run | ran | run |
| say | said | said |
| see | saw | seen |
| sell | sold | sold |
| send | sent | sent |
| show | showed | showed or shown |
| shut | shut | shut |
| sing | sang | sung |
| sink | sank | sunk |
| sit | sat | sat |
| sleep | slept | slept |
| speak | spoke | spoken |
| spend | spent | spent |
| stand | stood | stood |
| stink | stank | stunk |
| swim | swam | swum |
| take | took | taken |
| teach | taught | taught |
| tear | tore | torn |
| tell | told | told |
| think | thought | thought |
| throw | threw | thrown |
| understand | understood | understood |
| wake | woke | woken |
| wear | wore | worn |
| win | won | won |
| write | wrote | written |
3.6. Động từ khiếm khuyết (Modal verbs)
Động từ khiếm khuyết có vai trò bổ nghĩa cho động từ chính trong câu. Chúng ta sử dụng động từ khiếm khuyết để hình thành các câu như là: ‘Could you please open the window?’ hay ‘You should take your umbrella with you. It might rain.’.
Cấu trúc câu có sử dụng động từ khiếm khuyết sẽ có dạng như sau:
| Câu khẳng định: S + modal verb + V (nguyên mẫu) |
| Câu phủ định: S + modal verb + not + V (nguyên mẫu) |
| Câu nghi vấn: Modal verb + S + V (nguyên mẫu)? |
Tiếp theo chúng ta sẽ đến với cách dùng động từ khiếm khuyết (Modal verbs). Động từ khiếm khuyết thường được sử dụng để diễn đạt:
- Khả năng thực hiện một việc gì đó
Ví dụ minh hoạ: He can play basketball
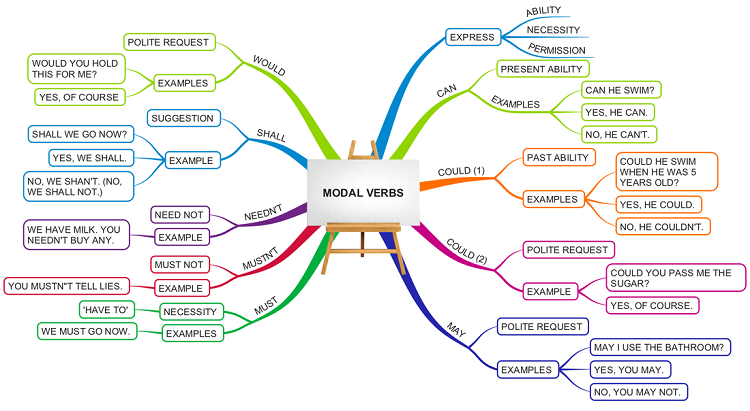
- Tỷ lệ/khả năng một việc gì đó sẽ xảy ra
Ví dụ minh hoạ: We might/ may lose the game if we don’t practice
- Sự bắt buộc/ cho phép làm một việc gì đó
Ví dụ minh hoạ: You mustn’t go out until you finish your homework.
- Lời khuyên với một người nào đó
Ví dụ minh hoạ: I think she should/ ought to take this chance
- Lời đề nghị/ yêu cầu đối với ai đó
Ví dụ minh hoạ: Would you like something to drink?/ May you pass me that bottle of ketchup?
- Một sự suy luận/ phỏng đoán
Ví dụ minh hoạ: Look how thick the snow is! It must be freezing outside.
Bên dưới là danh sách các động từ khiếm khuyết (Modal verbs) thường gặp trong tiếng Anh.
| Khẳng định | Phủ định | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Long forms | Contracted forms | Long forms | Contracted forms |
| can | — | cannot | can’t |
| could | — | could not | couldn’t |
| may | — | may not | — |
| might | — | might not | — |
| ought to | — | ought not to | oughtn’t to |
| need | — | need not | needn’t |
| shall | ‘ll | shall not | shan’t |
| should | ‘d | should not | shouldn’t |
| will | ‘ll | will not | won’t |
| would | ‘d | would not | wouldn’t |
4. Bài tập về Động từ (Verb) trong tiếng Anh
Bài tập
Bài tập 1: Chọn đáp án đúng nhất để hoàn thành các câu sau
1. They (build) ______________ a hotel in the city center last year.
A. build B. built C. building D. were built
2. Look! The bus (come) ______________.
A. comes B. coming C. is coming D. come
3. My parents are saving money because they (buy) ______________ a new house next year.
A. buy B. are buy C. buying D. are going to buy

4. We’ll go out when the rain (stop) ______________.
A. stops B. stopped C. is stopped D. stopping
5. Mr. An (be)______________ a doctor. He (work)______________ in a hospital.
A. is – worked B. was – worked C. is – works D. is – work
6. We (visit) ______________ our grandparents last week.
A. are visiting B. visited C. visiting D. visit
7. You should (go) ______________ to bed early.
A. go B. to go C. went D. going
8. ______________you (drive) ______________ a car?
A. Do – can drive B. Can – drive C. Did – can drive D. Can – do drive
9. My mother (not like) ______________ cats.
A. isn’t like B. don’t like C. doesn’t like D. isn’t liking
10. ______________she (prepare) ______________ her trip now?
A. Does – prepares B. Is – prepare
C. Is – preparing D. Does – prepare
Bài tập 2: Trong các câu sau đây, không phải câu nào cũng có lỗi sai. Tìm và sửa lỗi sai ở những câu có lỗi sai và nếu thấy câu nào đúng, hãy đánh dấu tick ().
1. My father used to giving me some good advice whenever I had a problem.
2. The sellers doesn’t want to sell things at a lower price.
3. If you don’t arrive soon, you did not have a seat in the conference.
4. There is differences and similarities between Vietnamese and American culture.
5. Let’s wait until the rain will stop.
6. George hasn’t completed the assignment yet, and Maria doesn’t, either.
7. There are many frequently mentioned reasons why one out of four arrests involve a juvenile.
8. Even though they are among the smallest carnivores, weasels will attacked animals that are twice their size.
9. Because of refraction, the water in a tank never looks as deeply as it actually is.
10. Today was such beautiful day that I couldn’t bring myself to complete all my chores.
Bài tập 3: Chia động từ ở thì phù hợp để hoàn thành một bài IELTS Writing Task 2 hoàn chỉnh
Caring for children is probably the most important job in any society. Because of this, all mothers and fathers should be required to take a course that prepares them to be good parents. To what extent do you agree or disagree with this view?
It (1-be)_______ true that parents shoulder a huge responsibility and that raising children is by no means an easy task. However, I completely disagree with the idea that we should therefore (2-force)___________all mothers and fathers to attend parenting courses.
In my opinion, the idea that all future parents should take a parenthood preparation course is completely impractical. Many prospective parents (3-have)__________jobs and busy schedules, and they may not be willing or able to attend regular parenting classes.
This (4-raise)__________ the question of whether those who missed the classes, or perhaps (5-refuse)__________ to attend, would be punished. I believe that it would be wrong to do this, and it would therefore be impossible to enforce the idea of compulsory training for parents. Besides, even if parents could be forced to attend, I doubt that people would agree on what good parenting entails, and so it would (6-be)_______difficult to create a parenting course to suit everyone.
As well as being impractical, I would argue that training courses for parents (7-be)________ unnecessary. Mothers and fathers (8-be)________ raising children without any formal help or official interference for thousands of years. Parenting skills are learnt from family members, friends, neighbors and the surrounding culture.
Perhaps more importantly, adults (9-learn)_________ to be good parents by instinct, by trial and error, and by getting to know their own children; for example, a good parent will try different strategies when faced with a badly-behaved child, and will gradually develop an understanding of what works to correct the behavior. None of this (10-require)___________ the intervention of a taught course.
In conclusion, while compulsory parenting lessons might seem like a good idea, I believe that such a scheme would be unworkable and largely pointless.
Đáp án
Bài tập 1
| 1. B | 2. C | 3. D | 4. A | 5. C | 6. B | 7. A | 8. B | 9. C | 10. C |
Bài tập 2
1. giving => give
2. doesn’t => don’t
3. did not => will not
4. is => are
5. will stop => stops
6. doesn’t => hasn’t
7. involve => involves
8. attacked => attack
9. deeply => deep
10. such beautiful day => such a beautiful day
Bài tập 3
1. is
2. force
3. have
4. raises
5. refused 6. be
7. are
8. have been
9. learn
10. requires
Động từ (verb) là một phần ngữ pháp không thể bỏ qua khi học tiếng Anh. Bài viết trên đã giúp bạn hiểu được lý thuyết cũng như bài tập về động từ trong tiếng Anh. Hãy rèn luyện thường xuyên để học tốt chủ điểm nay nhé. Duhoctms.edu.vn chúc các bạn học tập tốt.

Bình luận